Insurance is a contract in which one party, the insurer, agrees to compensate the other party, the insured, for losses or damages resulting from certain “covered” events. The insurer receives regular payments known as premiums from the insured in exchange for providing this coverage. In essence, insurance is a way of managing risk by pooling funds from many individuals to pay out claims when an unforeseen event occurs.
The most common types of insurance are life and health insurance, property and casualty (P&C) insurance, and liability insurance. Life and health policies cover medical bills and expenses associated with death or disability due to illness or injury; P&C policies protect against damage caused by natural disasters such as hurricanes or floods; while liability policies provide protection against legal liabilities incurred through negligence or intentional wrong-doing.
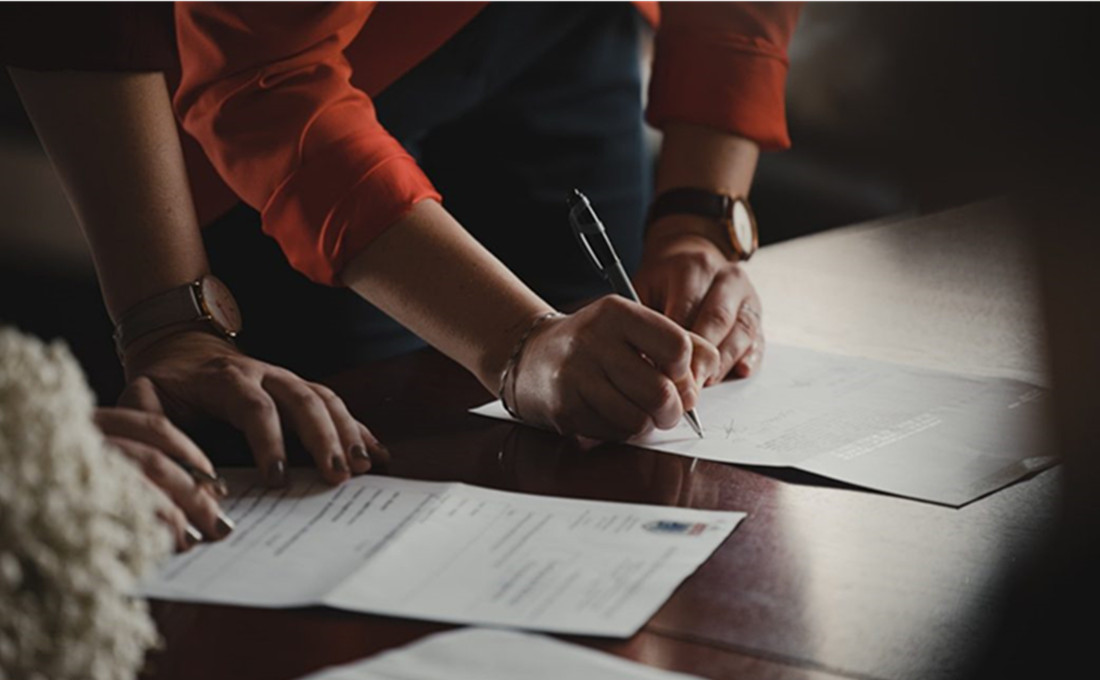

In order to receive coverage under an insurance policy, it is necessary for the insured to submit a claim after an event has occurred that meets certain criteria outlined in the policy documents. After verifying eligibility for benefits under the terms of an agreement between both parties, insurers may then proceed with paying out claims up to certain limits specified in the policy document.
Insurance serves multiple purposes: it provides financial security should unexpected events arise; helps individuals manage their own risks more effectively; can provide peace of mind knowing that if something happens there will be some form of compensation available; and acts as a safety net in case of financial hardship due to accidents or illnesses. Although not everyone needs every type of coverage offered by insurers – such as travel insurance – it is important to understand what types are available so you can make informed decisions about your personal circumstances when selecting a policy best suited for your needs.